GRIMP JAPAN 2025 was held in Marugame City, Japan, from February 16th to 18th. As one of Asia's
premier firefighting competitions, GRIMP JAPAN brought together firefighters from multiple countries
and regions around the world to compete fiercely in rope rescue, techniques and teamwork.
Here are some competition challenges and exciting moments.
I will provide a problem-solving approach for each task. This approach may not be the fastest, but it
can be accomplished using the most basic operations. The system diagrams are for conceptual
purposes only, and specific details must be adapted based on the actual on-site environment.
Task 1

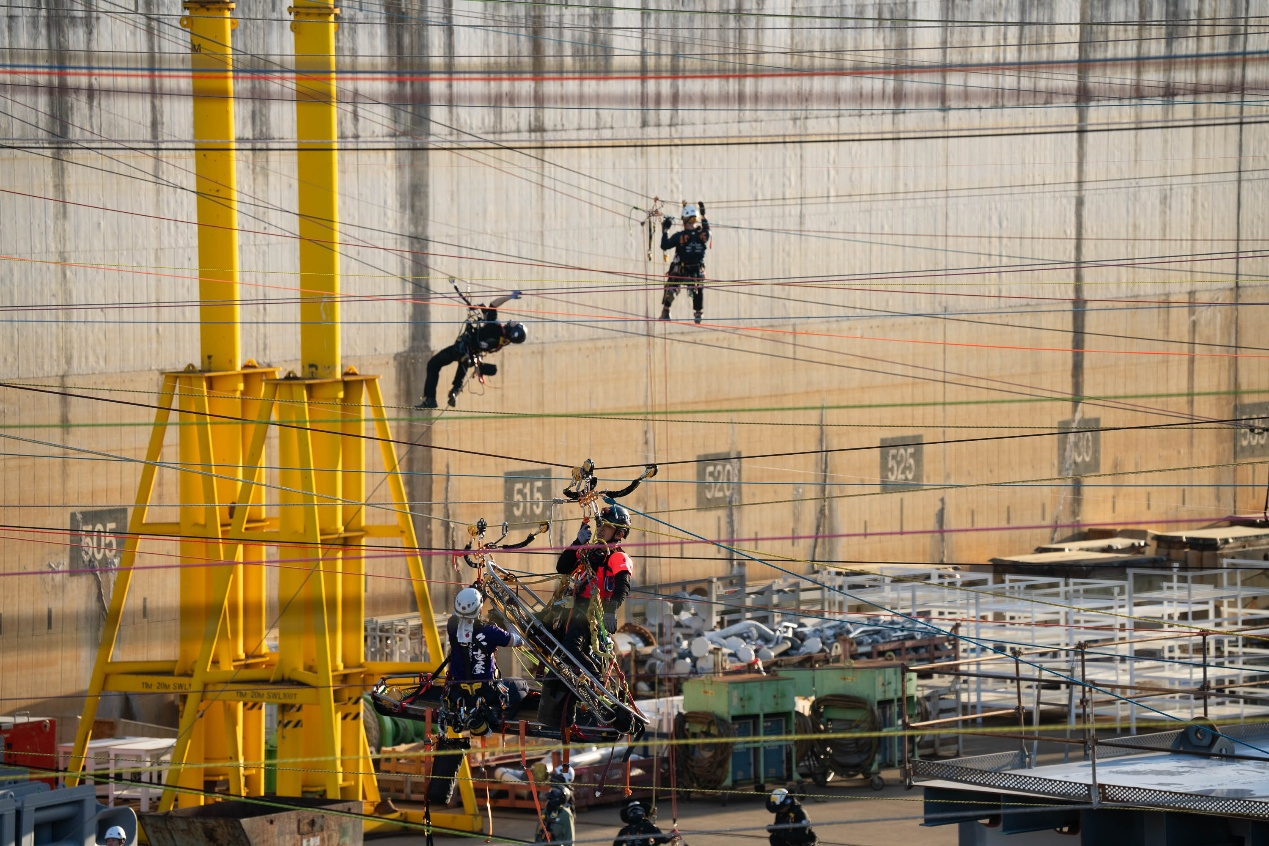
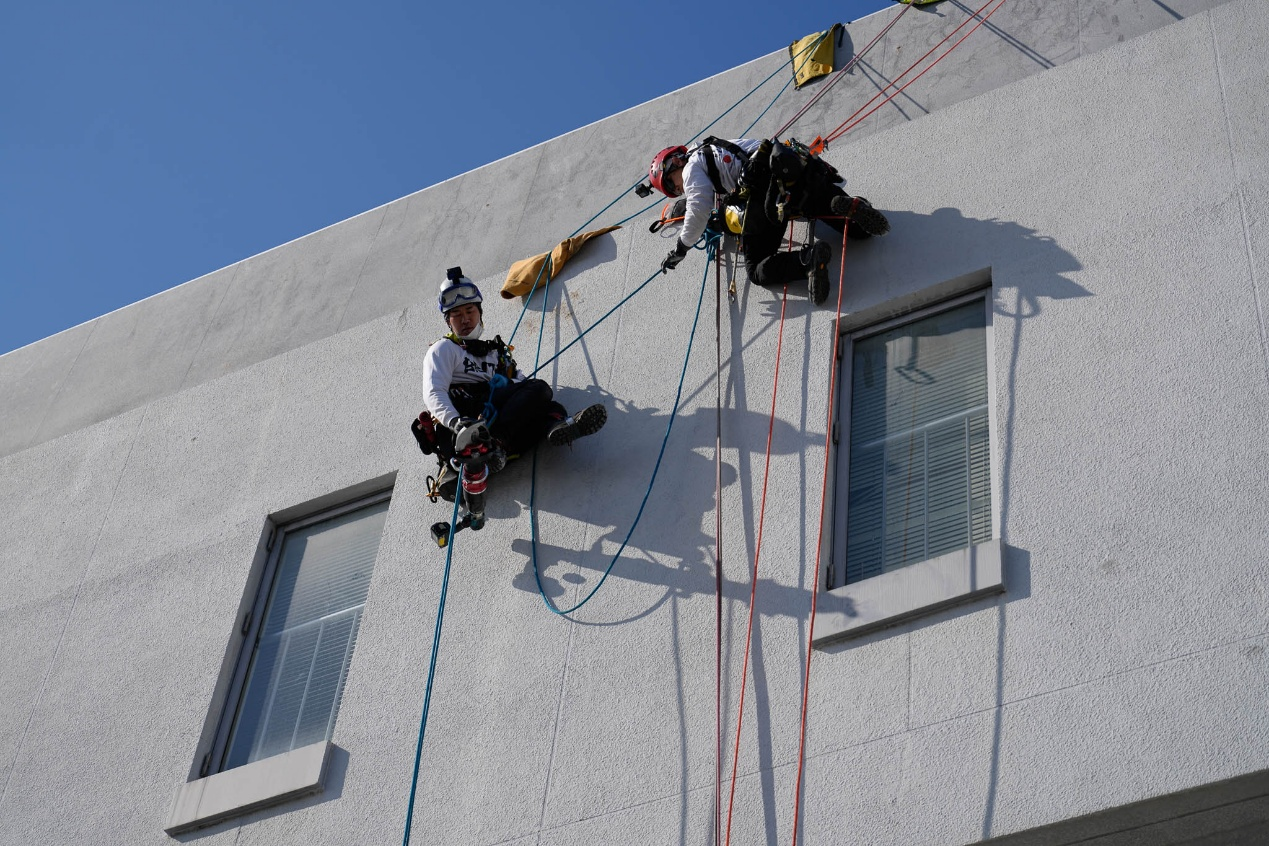
As the first task of the competition, it was held at a local shipyard. The operating range is very wide,
but the difficulty was relatively low, just like a warm-up challenge.
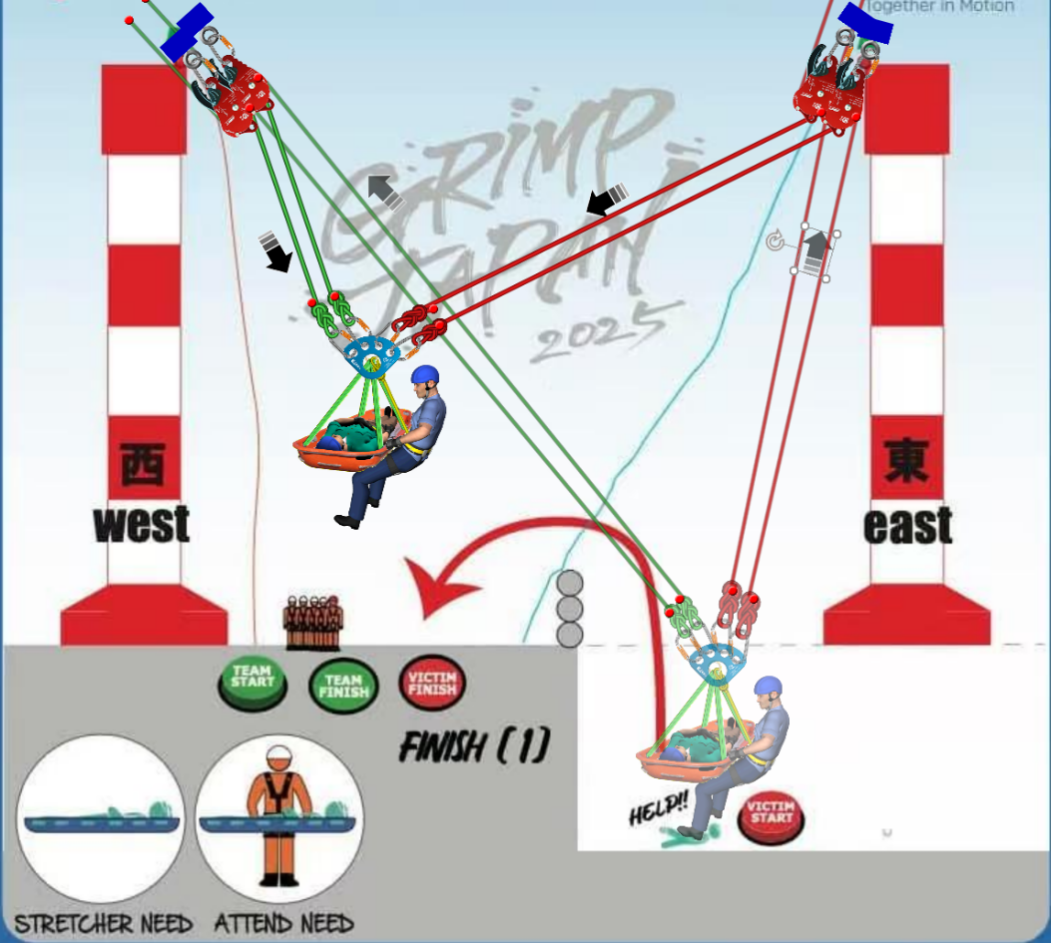
Problem-Solving Approach:
As shown in the image above, use RD2 devices on both sides overhead to set up a lifting and lowering
system. Cross-hauling can then be performed to complete this task. It is important to note that the
anchor points above may require operations on the rope, which significantly tests the capabilities of
the lifting team.
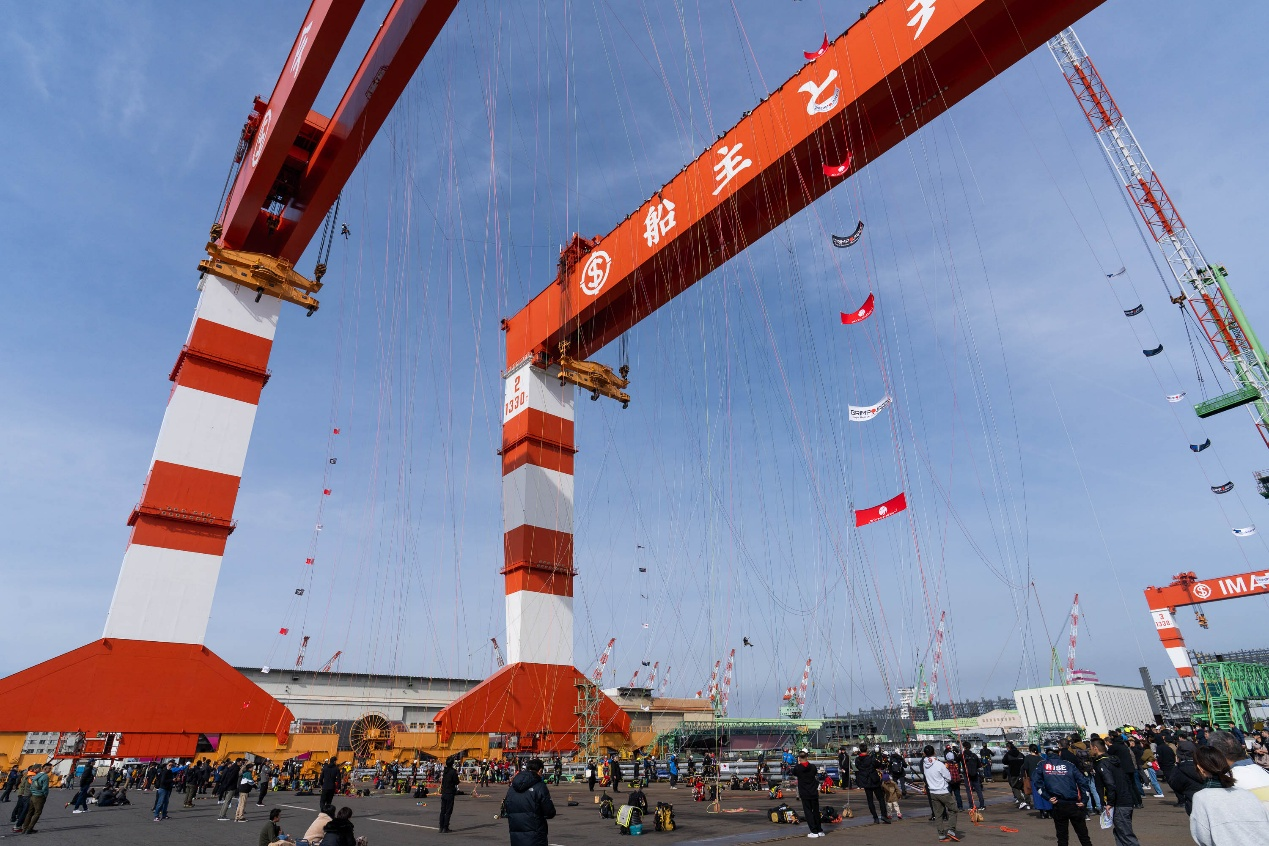

On site photo




- During lifting, edges may be encountered, requiring good coordination between both sides.
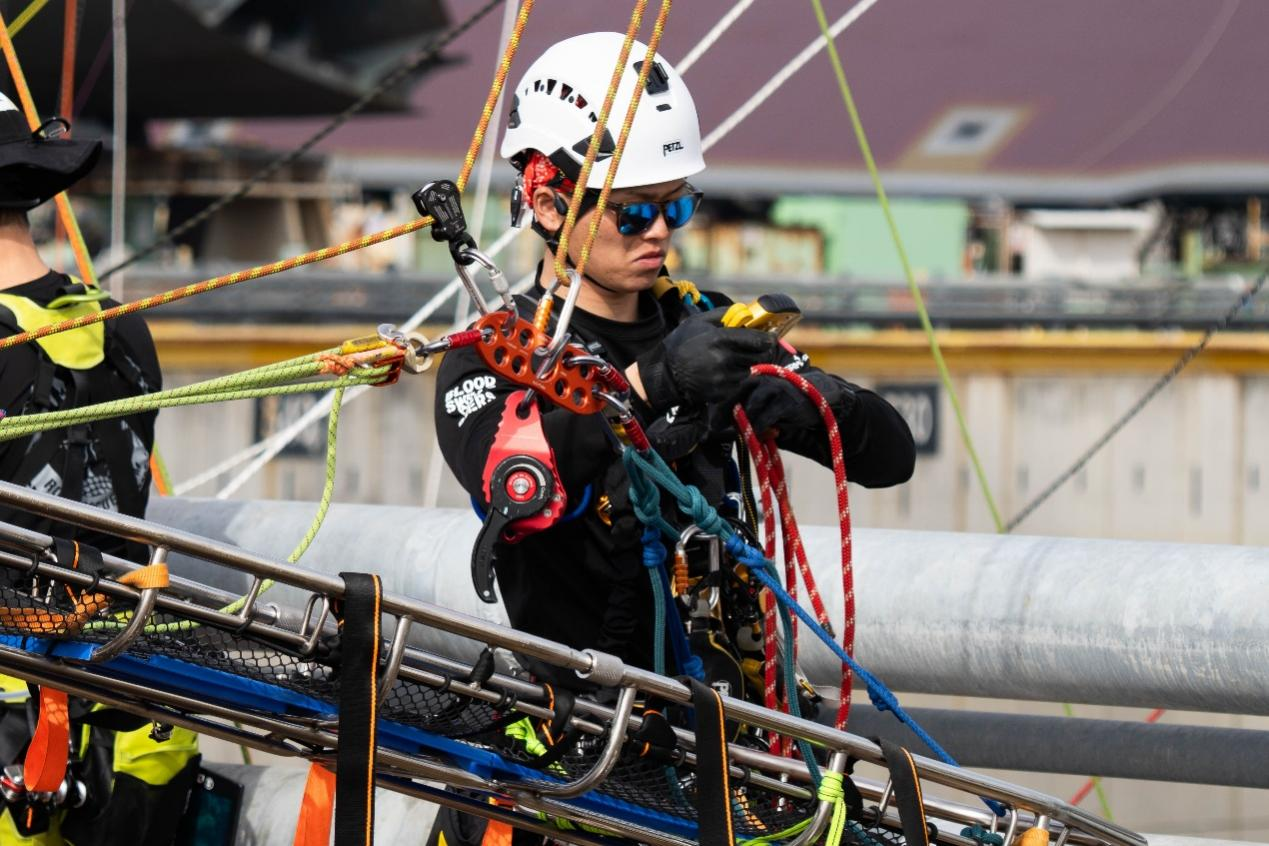

- Some teams also utilized specialized systems, as shown in the image above.

Task 2


As shown in the image above, anchor systems are established on both sides using guardrails, and
multiple RD2 devices are used at the starting point to set up a high-line system. Tighten the system,
build a REEVE system, and perform the lifting and lateral transfer of the stretcher. The diagram does
not show all backup measures; please decide how to add backups based on your own risk
assessment.

The high-line system requires rescue personnel to climb the rope to the opposite side.


The rope bridge, rigging plate, hauling rope, and REEVE rope utilize RD2 as the core controller for the
REEVE system.





For the anchor points on both sides, how to save space is a critical issue.
Task 3
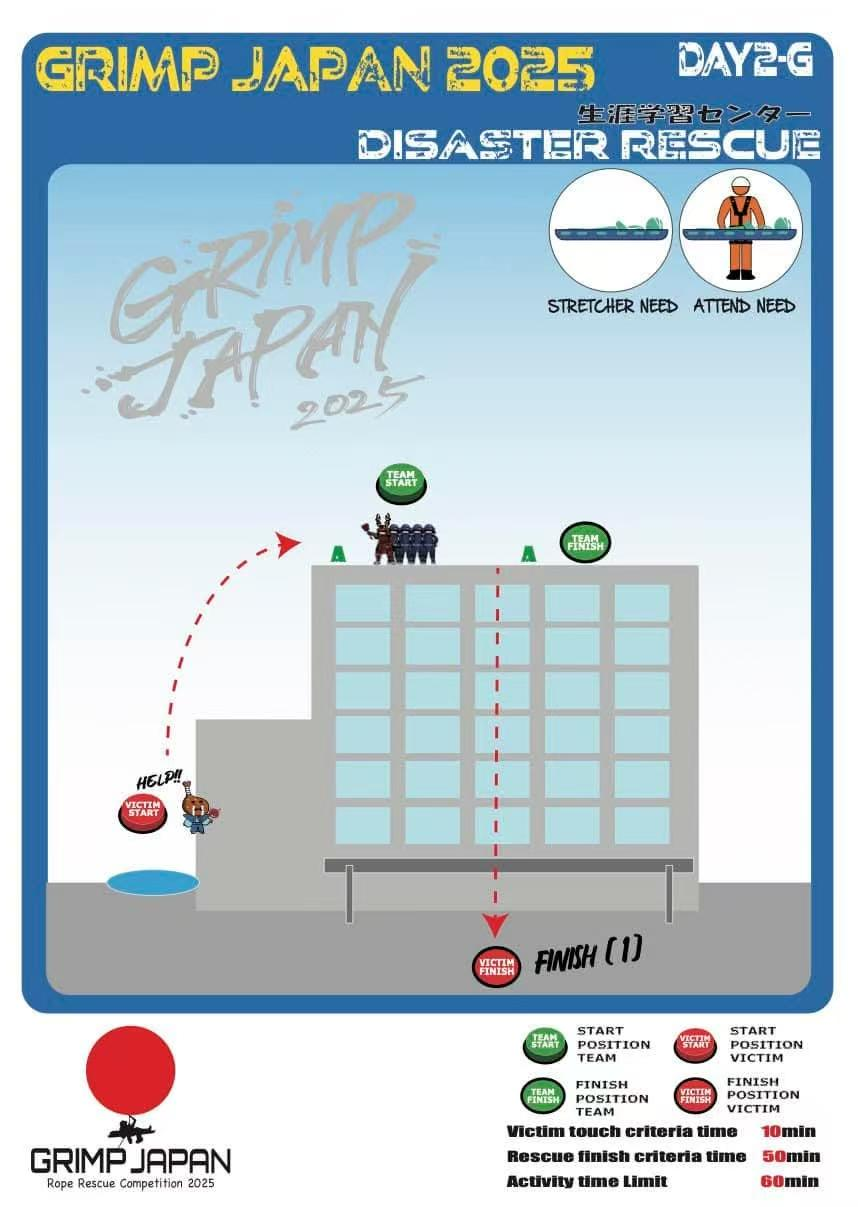
Problem-Solving Approach:
This task is of moderate difficulty. It requires lifting the casualty to the rooftop, then transferring to
the other side for lowering. It is important to note that the lifting phase involves wall in both
downward and upward angles.
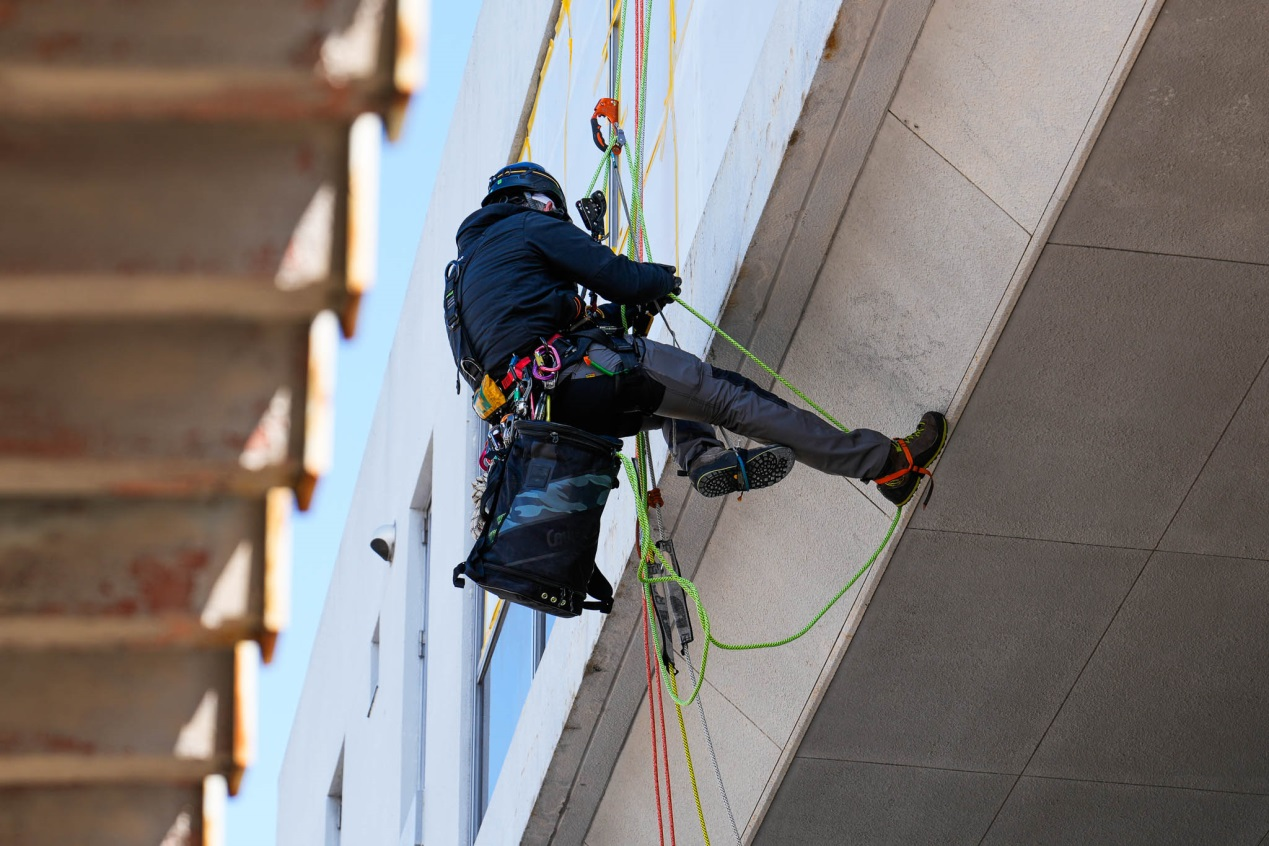

As shown in the image above, this is an upward-angle section. According to the competition rules,
direct friction between the rope and the edge is not allowed, as the casualty is positioned very close
below. It is recommended that the accompanying personnel act as a human deviation here.
Alternatively, a rope protector pad can be directly fixed in place.



Task 4

Problem-Solving Approach:
In terms of rope operations, this challenge is not significantly different from the previous two. It
involves setting up anchor points and a lifting system on the rooftop to hoist the casualty to the top.
Therefore, there is no particularly unique method required. The main difficulty lies in overcoming the
roof edge. However, setting up the anchor points is relatively straightforward since the organizer has
set three hangers.
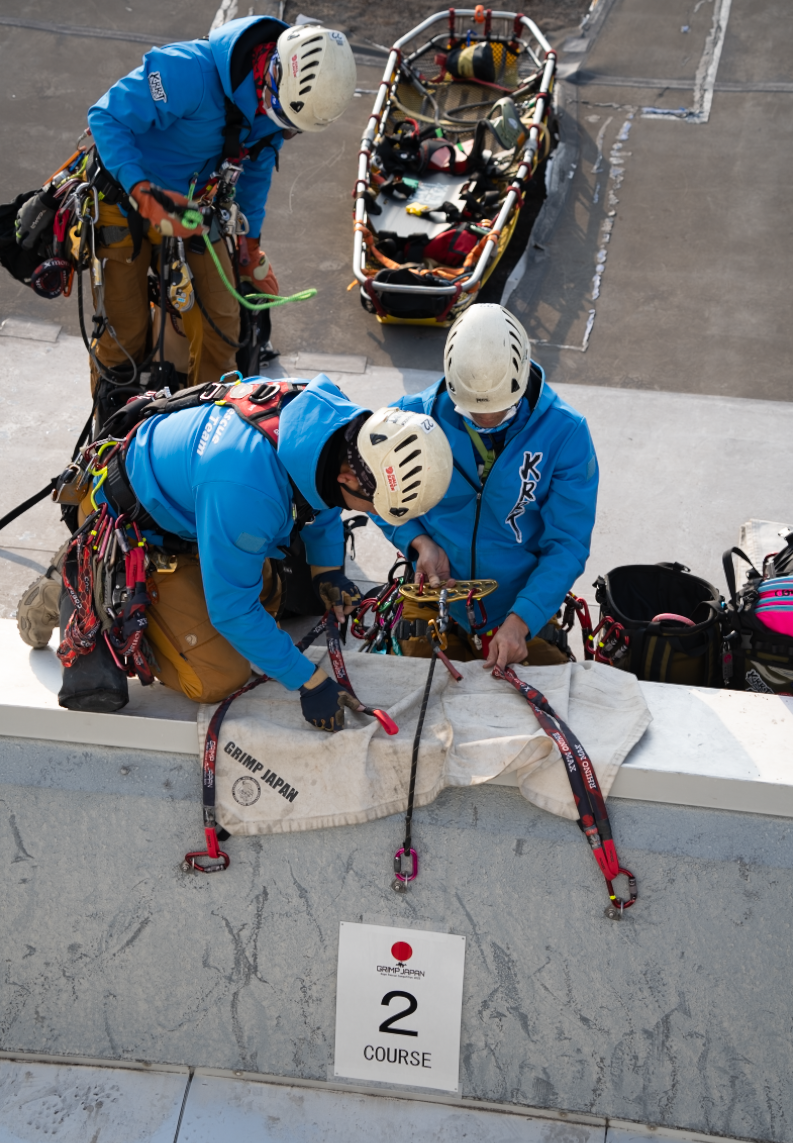

The anchor devices set up by the organizer allow each participating team to simply use them to build
their anchor systems.
What sets this task apart from the others is that it requires teams to use hydraulic rescue tools to
break into a vehicle. This highlights the fact that rescue team members must be proficient in a variety
of rescue skills, with rope techniques being just one of them.
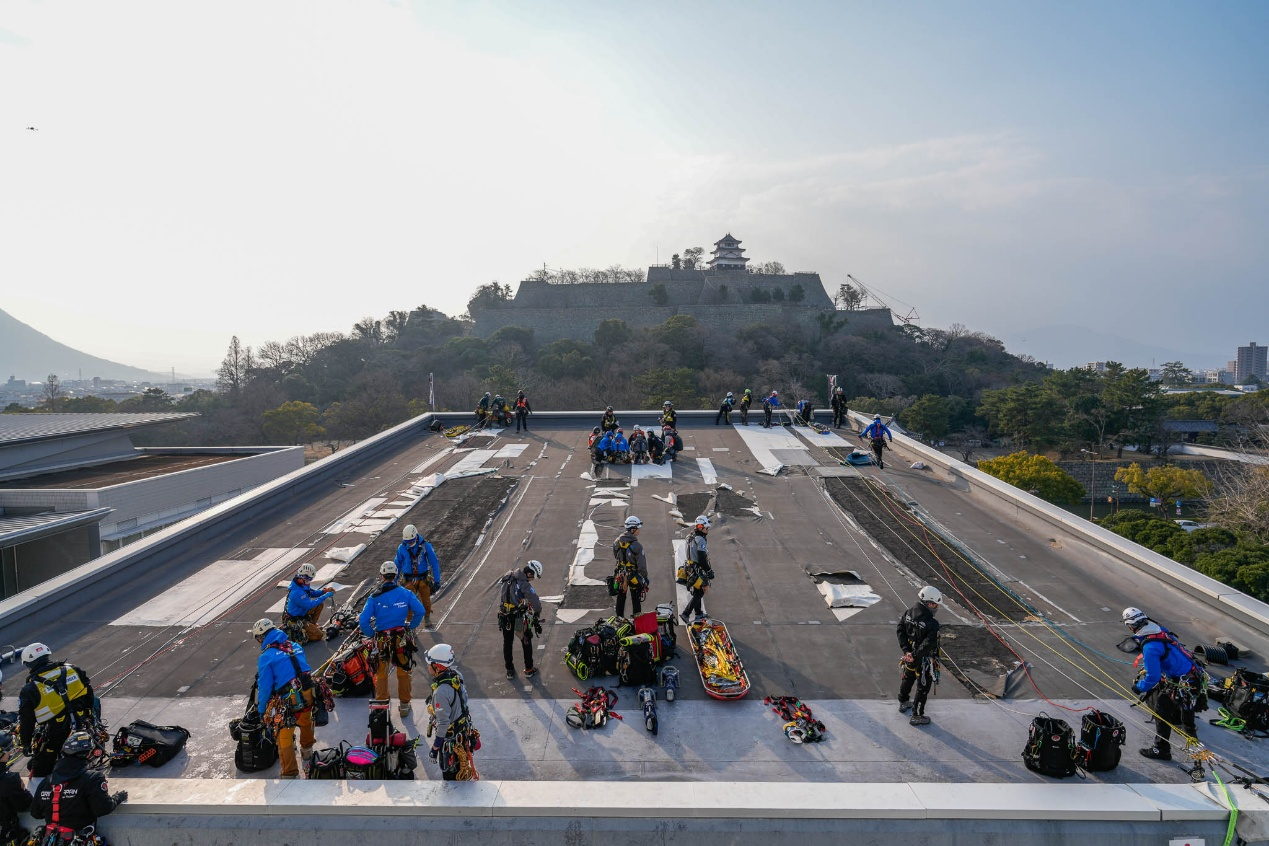

From the rooftop environment, you can see the iconic landmark of Marugame City—Marugame Castle.


The rooftop is spacious enough to allow rescue personnel to perform lifting operations comfortably.



A stepped edge with a large angle, making it relatively easy to pass through.
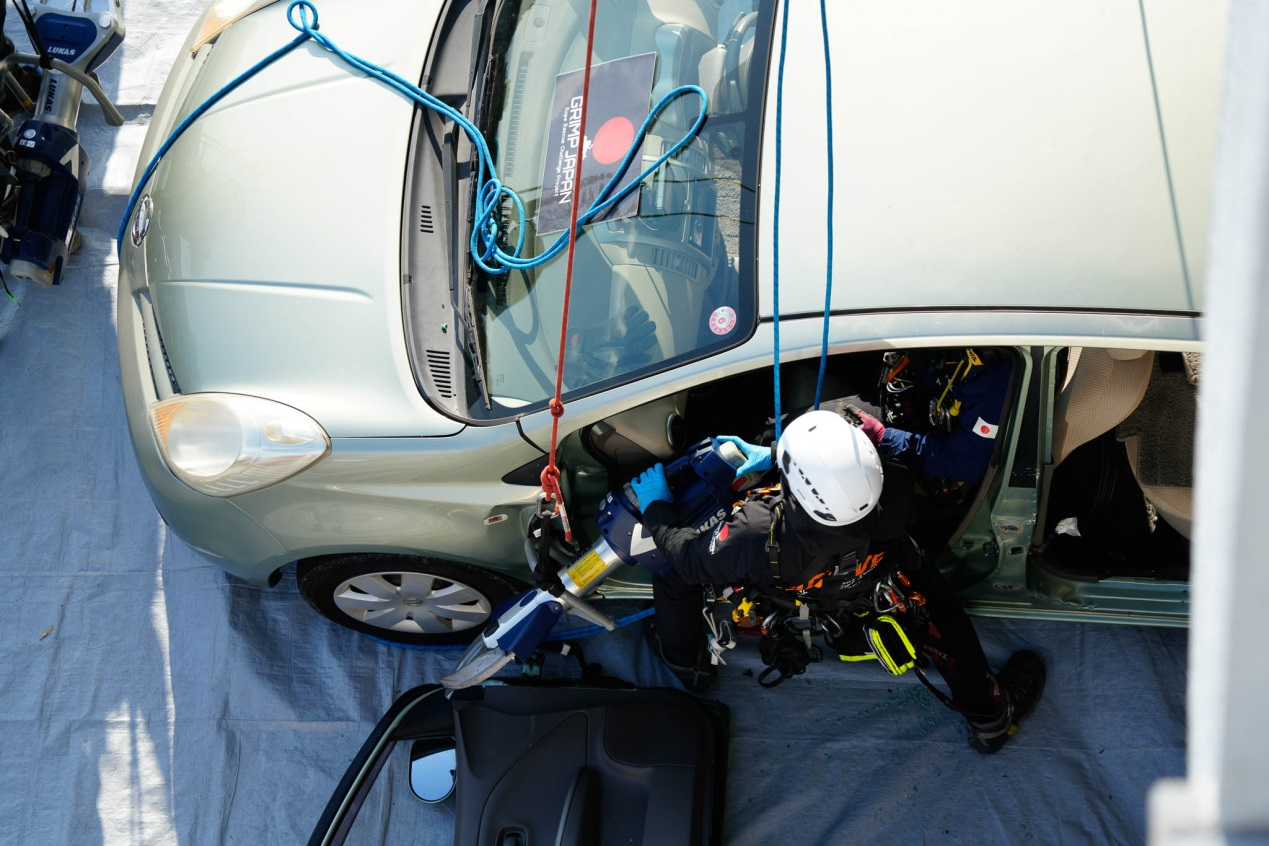

Vehicle dismantling in progress.
Task 5
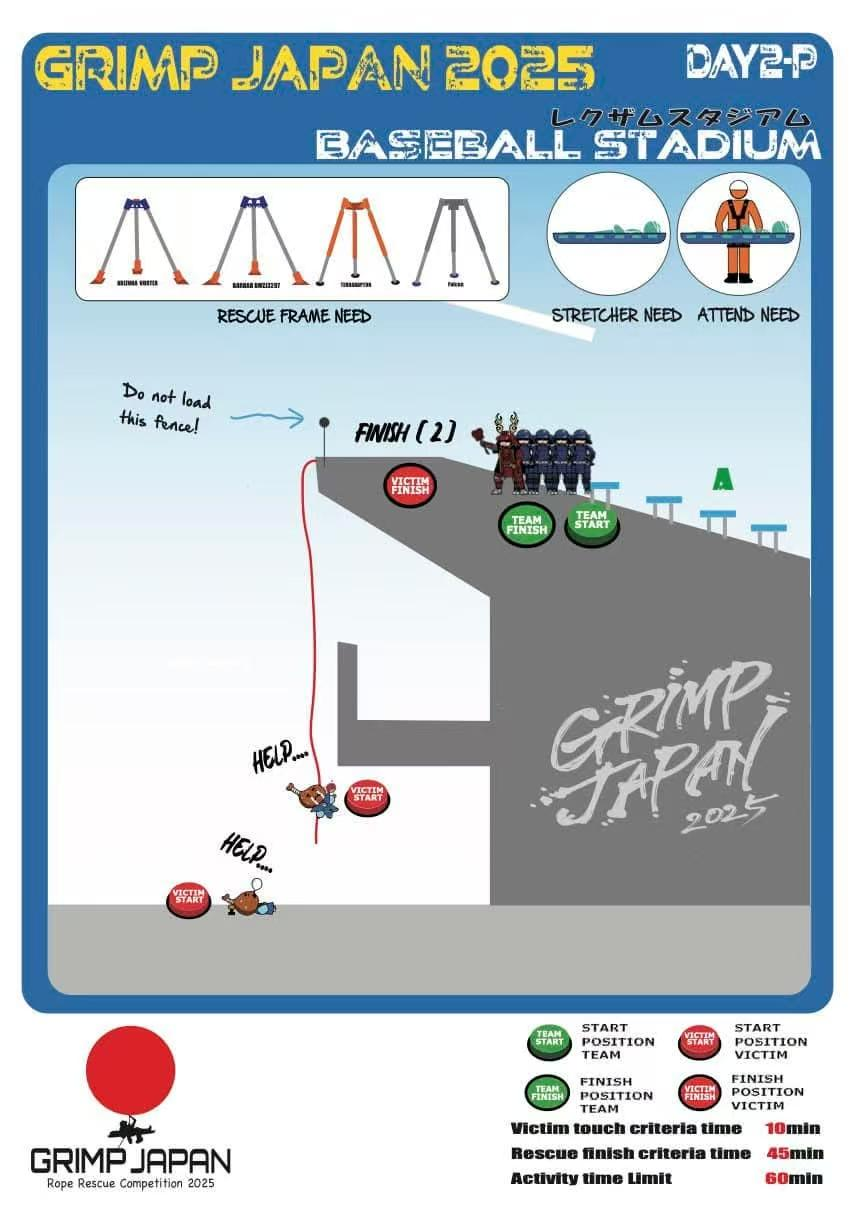
Problem-Solving Approach:
Use a tripod to create an artificial high-directional anchor point, which facilitates the stretcher's
passage over the edge. Simply set up a lifting system using RD2 inside the venue to hoist the
stretcher.
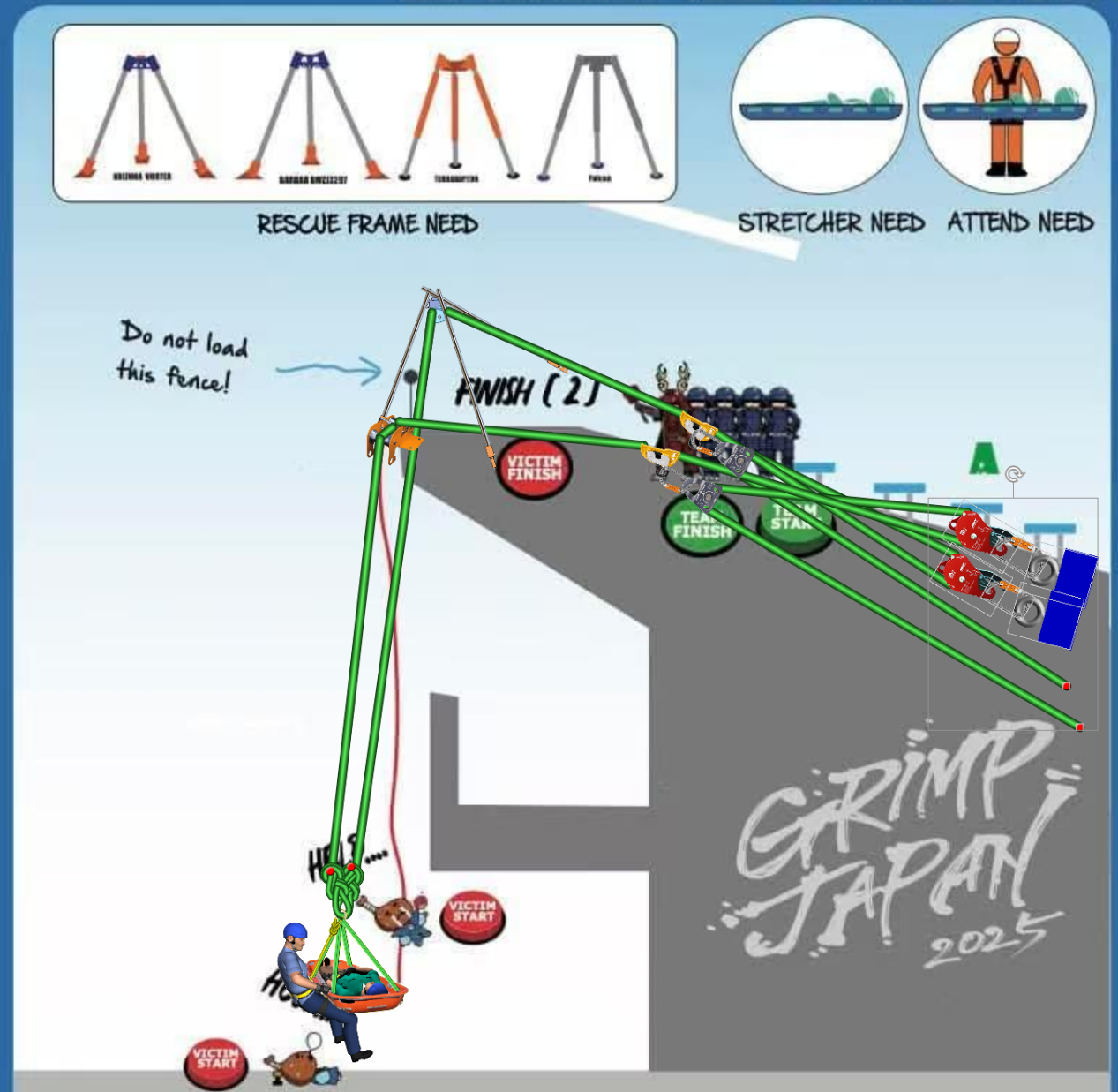
The main challenge of this task lies in setting up the tripod and overcoming an obstacle beneath the
eaves. This requires the stretcher attendant to flexibly adjust their posture to assist the stretcher in
navigating past the obstacle.

The use of a tripod allows the stretcher to pass over the edge with ease.
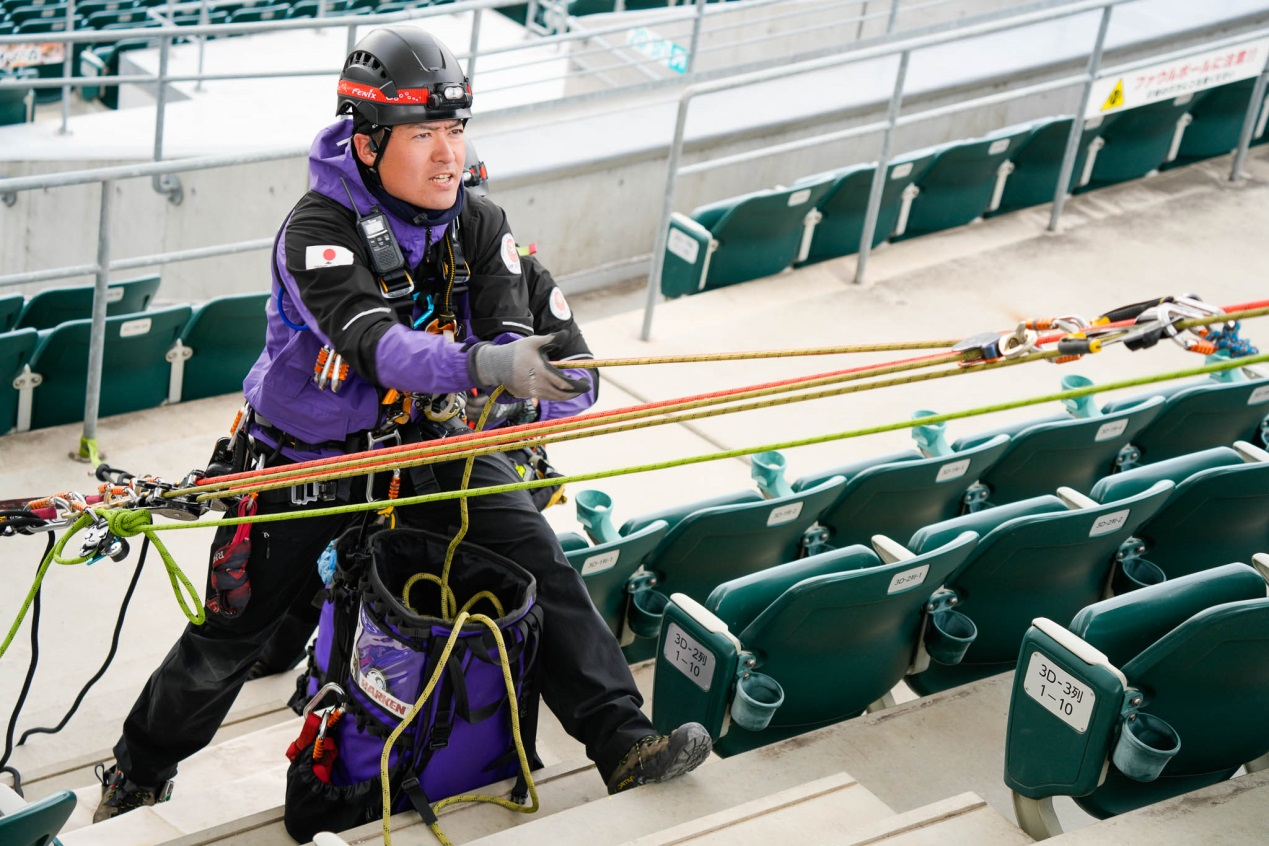

The lifting system consists of a standard pulley system.
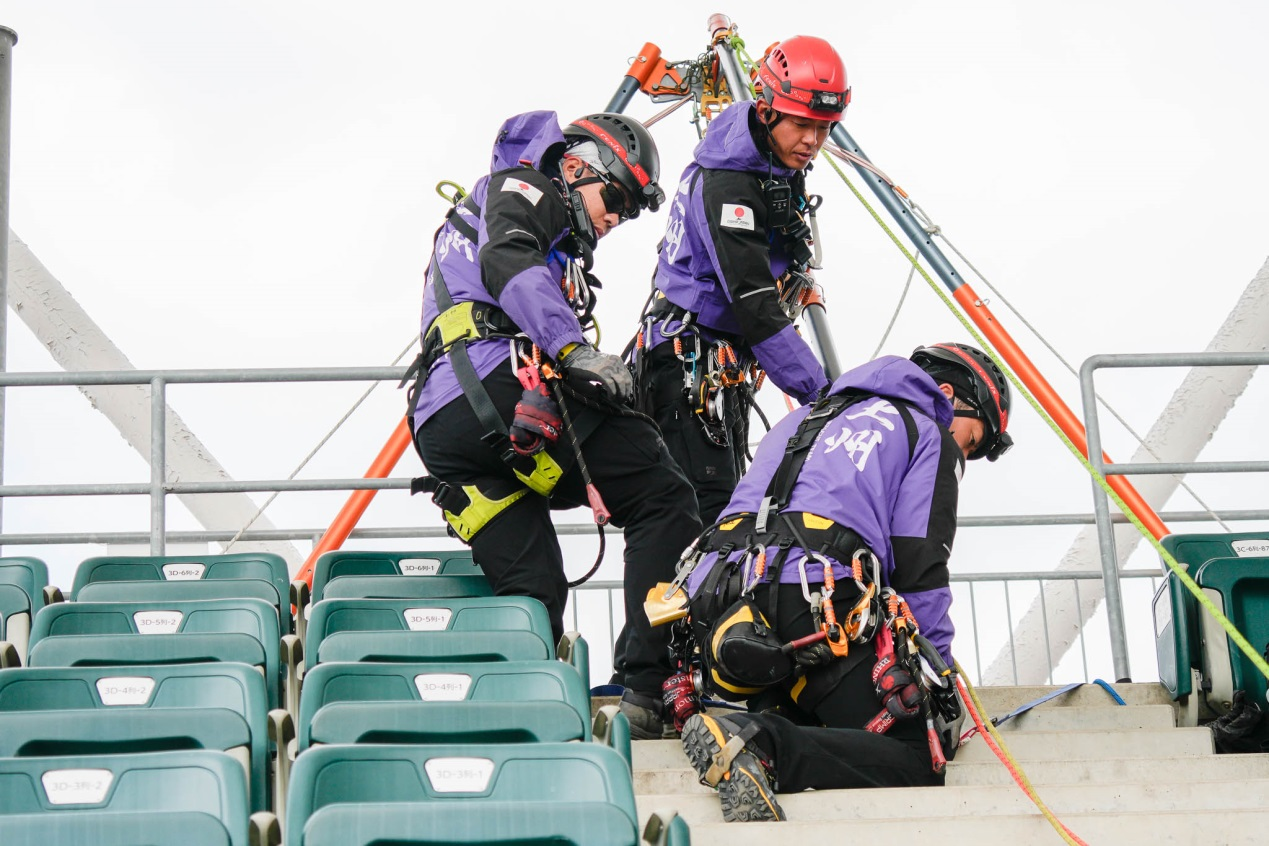

This event highlighted the importance of rope techniques, solutions, and teamwork in rescue.
Stay tuned for more exciting content in the next article!
ASAT – Always Safe, Always Trusted.
